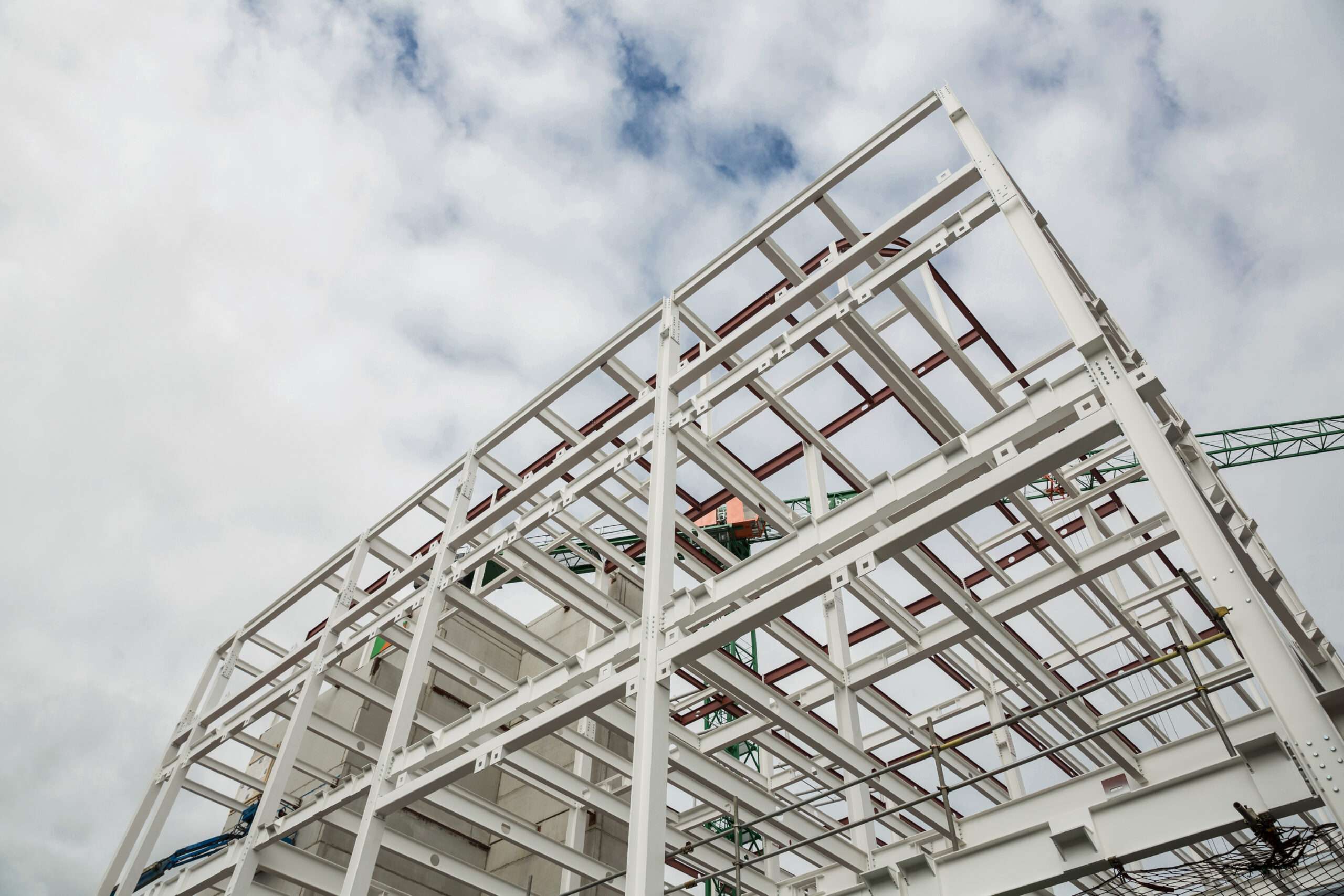
The metal building industry is a major driving force in the global construction sector, boasting a global market size exceeding USD 16 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 22.3 billion by 2030. Its reach extends far beyond mere numbers, impacting economies and landscapes alike.
The industry generates significant economic activity, employing thousands directly through manufacturing, construction, and engineering jobs. Furthermore, its cost-effective and efficient construction practices benefit businesses by reducing construction time and lowering overall project costs. This in turn stimulates investments and fosters economic growth.

Definition of a Metal Building: components, types, applications
A metal building is a pre-engineered structure primarily constructed from steel or aluminum. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar buildings, the components are prefabricated in controlled factory environments, ensuring precision and efficiency. Here’s a breakdown of its key elements:
Primary framing This forms the backbone of the building, consisting of steel beams and columns that provide structural support.
Secondary framing This includes purlins, girts, and trusses that support the roof and wall panels.
Enclosure Metal panels made from steel or aluminum form the walls and roof, offering weather protection and insulation.
Doors and windows These complete the building envelope and can be customized to meet specific needs.
Types of metal buildings
Clear span buildings Large, open spaces without interior columns, ideal for warehouses and distribution centers.
Rigid frame buildings Offer a versatile design with sloped roofs for efficient drainage.
Monoslope buildings Feature a single-sloped roof, often used for agricultural buildings and storage facilities.
Custom-designed buildings Can be tailored to unique architectural requirements and specific functional needs.
Applications
Commercial buildings Warehouses, distribution centers, retail stores, offices, car dealerships.
Industrial buildings Factories, workshops, power plants, manufacturing facilities.
Agricultural buildings Barns, greenhouses, storage sheds, grain silos.
Public buildings Schools, libraries, community centers, sports facilities.
Recreational buildings Churches, gyms, arenas, event spaces.
This is just a glimpse into the dynamic world of metal buildings. By diving deeper into each element and application, you can uncover the remarkable story of how metal shapes our built environment and propels economic growth.

Key Players in the Metal Building Industry
Metal Building Manufacturers
Major Players
North America Nucor Building Systems, Butler Manufacturing, Varco Pruden Buildings, Kirby Building Systems, W.W. Clyde Company
Europe ArcelorMittal Construction, Tata Steel Building Products, Kingspan Group, Lindab Group
Asia Dongfang Special Steel Group, BlueScope Steel, CGL Metal Structures, Jingye Real Estate Group
Regional Variations
North America Dominated by large, vertically integrated companies that manufacture steel and build structures.
Europe More fragmented market with regional players and a focus on custom-designed buildings.
Asia Rapidly growing market with a mix of established players and emerging manufacturers.
Metal Building Suppliers
Distributors and Dealers
Act as intermediaries between manufacturers and contractors, typically serving specific geographic regions.
Offer sales, technical support, and inventory management services.
May specialize in certain types of metal buildings or applications.
Online Retailers
Growing segment offering direct-to-contractor sales and wider product availability.
Convenient for smaller projects and readily accessible information.
Often focus on standardized building kits with customizable options.
Metal Building Contractors
Design and Engineering Services
Work with architects and engineers to develop construction plans and specifications.
Handle foundation preparation, building erection, and finishing work.
Offer expertise in metal building construction best practices.
Construction Services
Provide project management, site preparation, erection crews, and equipment.
Offer turnkey solutions that handle the entire construction process.
Can specialize in specific applications like agricultural or commercial buildings.
Architects and Engineers
Specializing in Metal Building Design
Understand the unique properties and advantages of metal buildings.
Focus on efficient design, maximizing space utilization and minimizing materials.
Contribute to innovative architectural solutions tailored for metal construction.
Roles and Responsibilities
Develop initial building concepts and schematics.
Perform structural calculations and ensure code compliance.
Create detailed construction drawings and specifications.
Additional Considerations
The complexity of projects often dictates the level of involvement from each player.
Smaller projects may involve direct interaction with manufacturers or suppliers, while larger ones require collaboration between all key players.
New technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) are streamlining communication and collaboration within the metal building industry.
By understanding the diverse roles and expertise of each player, we gain a deeper appreciation for the collaborative nature of the metal building industry. Whether it’s a small barn or a sprawling warehouse, these intricate partnerships bring innovative, efficient, and sustainable building solutions to life.

Advantages of Metal Buildings
Cost-effectiveness
Lower Material Costs Steel and aluminum are often cheaper than traditional building materials like brick, concrete, and wood.
Reduced Labor Costs Prefabricated components require less on-site labor, decreasing project timelines and associated costs.
Minimal Foundation Requirements Metal buildings often require shallower and less complex foundations compared to traditional structures, further reducing costs.
Tax Advantages In some regions, metal buildings might qualify for tax incentives due to their faster depreciation rates.
Durability
Weather Resistance Steel and aluminum resist elements like wind, rain, snow, and UV rays, minimizing upkeep and repair costs.
Fire Resilience Many metal buildings have inherent fire-resistant properties, enhancing safety and potentially lowering insurance premiums.
Pest and Termite Resistance Unlike wood, metal is impervious to pests and termites, eliminating a significant maintenance concern.
Longevity With proper maintenance, metal buildings can last for decades, offering a long-term return on investment.
Speed of Construction
Prefabricated Components Pre-manufactured walls, roof panels, and framing systems arrive ready for assembly, significantly reducing construction time.
Modular Design Building components can be modularly added or removed as needed, offering flexibility and future expansion possibilities.
Minimal Disruption Quicker construction minimizes disruption to ongoing business operations or surrounding activities.
Early Occupancy Faster completion allows earlier occupancy and quicker ROI for businesses or revenue generation for rental properties.
Sustainability
Recyclable Materials Steel and aluminum are highly recyclable, minimizing environmental impact during demolition or renovation.
Energy-efficient Design Metal buildings can be designed with features like reflective roofs, insulated panels, and natural daylight strategies, reducing energy consumption.
Reduced Resource Use Prefabrication minimizes construction waste and material consumption compared to traditional building methods.
Certifications Many metal buildings achieve green certifications like LEED, providing further sustainability recognition.
Versatility
Wide Range of Applications From warehouses and factories to schools and churches, metal buildings can adapt to diverse functional needs.
Customizable Design Building components and configurations can be tailored to suit specific architectural requirements and aesthetics.
Clear Span Interiors Open floor plans without interior columns offer flexibility for layout and space utilization.
Easy Expansion Modular design allows for future expansion or modification as needs evolve.
These advantages combine to make metal buildings a compelling choice for a wide range of projects. By understanding the economic, performance, and environmental benefits they offer, we can see how they contribute to a more efficient, sustainable, and adaptable built environment.

A panorama of metal building
Applications of Metal Buildings: Shaping Landscapes Across Industries
Metal buildings are not just versatile; they’re transforming diverse landscapes across an array of industries. Let’s dive deeper into their specific applications
Commercial Buildings
Warehouses and Distribution Centers
Spacious interiors Clear-span designs provide unobstructed storage for large volumes of goods and efficient logistics operations.
Durability Withstands heavy loads and withstands harsh weather conditions for long-lasting performance.
Cost-effectiveness Prefabricated construction and minimal maintenance translate to lower overall costs.
Image Modern metal building designs can enhance brand image and project a professional impression.
Retail Stores
Flexibility Adaptable to various store layouts and configurations, accommodating diverse product lines and brand aesthetics.
Scalability Easy to expand or modify as businesses grow or evolve.
Natural lighting Metal buildings can incorporate skylights and large windows for bright, energy-efficient spaces.
Cost-competitiveness Offers an affordable alternative to traditional brick-and-mortar retail buildings.
Offices
Open floor plans Clear-span interiors enable flexible office layouts and promote collaboration.
Modern aesthetics Metal buildings can be designed with contemporary finishes and architectural elements for a stylish workspace.
Sustainable options Metal buildings can integrate energy-efficient features for environmentally conscious work environments.
Quick construction Minimizes business disruption and allows for faster occupancy.
Industrial Buildings
Factories and Workshops
Strength and durability Withstands heavy machinery and manufacturing processes.
Expandability Adapts to production needs with modular additions or modifications.
Controlled environments Metal buildings can be insulated and temperature-controlled for optimal manufacturing conditions.
Fire resistance Offers inherent fire protection for enhanced safety.
Power Plants and Energy Facilities
Weather resistance Protects sensitive equipment from harsh weather conditions.
Customizable design Accommodates specific requirements for ventilation, power generation, and equipment access.
Scalability Easily expands or adapts to accommodate future infrastructure needs.
Durability Provides long-term value and protection for critical energy infrastructure.
Agricultural Buildings
Barns and Livestock Shelters
Spacious interiors Provides ample space for animals to roam and thrive.
Ventilation and natural light Metal buildings can be designed with optimal air circulation and natural daylighting for animal well-being.
Pest and rodent resistance Metal construction minimizes risk of pest infestations and diseases.
Durability Withstands harsh weather conditions and wear and tear from livestock.
Greenhouses and Hydroponic Farms
Controlled environments Metal buildings offer excellent insulation and climate control for optimal plant growth.
Durability Withstands high humidity and weather fluctuations.
Scalability Easy to expand or modify as agricultural needs evolve.
Cost-effectiveness Affordable construction option compared to traditional greenhouses.
Public Buildings
Schools and Libraries
Open and bright spaces Large, clear-span interiors create flexible learning environments with ample natural light.
Durability and safety:Withstands wear and tear and provides inherent fire resistance for student safety.
Cost-effective solution Offers an affordable alternative to traditional school buildings.
Sustainability Metal buildings can integrate energy-efficient features for environmentally conscious learning.
Community Centers and Sports Facilities
Multifunctional spaces Adapts to various events and activities from community gatherings to athletic competitions.
Acoustics and lighting Design options cater to specific needs for sound systems, lighting, and spectator seating.
Accessibility Metal buildings can be designed to meet accessibility standards for all users.
Durability Withstands heavy traffic and use for long-term value.
Trends and Innovations in the Metal Building Industry: Shaping the Future with Steel and Smarts
The metal building industry isn’t merely evolving; it’s undergoing a paradigm shift, fueled by groundbreaking advancements that redefine possibilities and blur the lines between functionality and aesthetics. Let’s delve deeper into these dynamic trends:
Technological Advancements: From Pixels to Performance
3D Modeling and Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Architects and engineers sculpt virtual replicas of metal buildings, optimizing design, minimizing errors, and streamlining construction.
Imagine clash detection software alerting them to potential conflicts between pipes and wires before a wrench is wielded.
BIM fosters seamless collaboration between stakeholders, from architects to contractors, ensuring a smoother building journey.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Clients can step into virtual renditions of their future buildings, experiencing spatial relationships and exploring design options like never before.
Contractors can train using VR simulations, practicing assembly procedures and safety protocols in a risk-free environment.
AR overlays digital information onto physical sites, guiding construction crews and facilitating precise installations.
Sustainable Design Practices: Greening the Steel Landscape
Energy-efficient Materials
Advanced insulation panels and reflective roof coatings minimize energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Strategically placed windows and skylights maximize natural daylight, reducing reliance on artificial lighting.
Look for innovative materials like bio-based insulation or recycled steel, lowering the embodied carbon footprint.
Renewable Energy Integration
Solar panels seamlessly integrated into roofs or facades transform metal buildings into power generators.
Wind turbines and other renewable energy sources can be incorporated for even greater energy independence.
Smart design strategies like passive cooling and natural ventilation further reduce reliance on mechanical systems.
Smart Building Technologies: Brains for the Brawn
Building Automation and Control Systems
Lights, HVAC, and other systems dance to the tune of automated schedules and occupant preferences, optimizing energy use and comfort.
Real-time data on temperature, humidity, and air quality empowers informed decisions and proactive maintenance.
Imagine an entire warehouse adjusting its temperature based on inventory levels and worker activity.
Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
Building performance is monitored remotely, with sensors keeping a watchful eye on vital signs like energy consumption and equipment health.
Predictive maintenance algorithms anticipate potential issues, preventing costly downtime and ensuring smooth operations.
Picture technicians troubleshooting glitches remotely, minimizing disruptions and keeping operations running like clockwork.
Customization and Personalization From Ordinary to Extraordinary
Architectural Creativity
Metal buildings shed their utilitarian skin, embracing sleek curves, textured facades, and architectural flourishes.
Imagine metal buildings seamlessly blending into historic districts or standing out as contemporary landmarks.
Green walls and integrated landscaping add a touch of nature, blurring the lines between building and environment.
Interior Optimization
Modular walls and flexible layouts morph to accommodate diverse needs, from spacious workshops to cozy cafes.
Soaring ceilings and open floor plans foster a sense of openness and collaboration.
High-tech infrastructure and modern amenities make metal buildings ideal for cutting-edge workspaces and contemporary living environments.
These trends are not just buzzwords; they’re transforming the landscape of the metal building industry. By embracing technology, sustainability, and personalized design, steel is becoming more than just a material; it’s a canvas for shaping environments that are efficient, innovative, and visually captivating. The future of metal buildings is brimming with possibilities, limited only by the imagination of architects, engineers, and owners alike.

Challenges and Opportunities in the Metal Building Industry: Navigating the Steel Sea
While the metal building industry enjoys a surge of innovation and potential, it’s not without its fair share of challenges. Understanding these obstacles and capitalizing on emerging opportunities are crucial for the industry’s continued success. Let’s explore both sides of the coin.
Competition from Traditional Building Materials and Methods
Brick and mortar For some projects, the aesthetic appeal and perceived durability of traditional materials like brick and concrete remain appealing.
Wood framing In certain regions, familiarity with wood construction and readily available timber resources present competition.
Overcoming misconceptions Stereotypes of metal buildings being purely utilitarian or lacking the design flexibility of traditional materials still persist.
Fluctuations in Steel Prices and Availability
Volatile steel market Global economic factors and supply chain disruptions can lead to sharp swings in steel prices, impacting project costs and profitability.
Material shortages Sudden spikes in demand or logistical bottlenecks can create temporary shortages of specific steel components, delaying construction schedules.
Hedging strategies Employing smart purchasing strategies and alternative material options can mitigate the impact of price fluctuations.
Increasing Demand for Sustainable and Energy-efficient Buildings
Stringent regulations Rising environmental concerns and stricter energy efficiency standards push the industry to adopt sustainable practices and materials.
Life-cycle analysis Embracing a life-cycle perspective that considers the environmental impact of materials beyond initial construction costs is crucial.
Green certifications Integrating renewable energy sources, recycled materials, and energy-efficient design into metal buildings can unlock opportunities for green certifications.
Workforce Shortages in Skilled Trades
Aging workforce An aging workforce in construction trades leads to a smaller pool of skilled labor, especially in specialized areas like metal building erection.
Attracting new talent Implementing competitive wages, training programs, and apprenticeship opportunities can attract young talent to the industry.
Automation and technology Integrating advanced technologies like robotics and automated construction processes can partially offset labor shortages.
Opportunities for Growth in Emerging Markets and Specialized Applications
Developing economies Growing demand for infrastructure and buildings in developing economies presents significant growth potential for the metal building industry.
Niche markets Specializing in specific applications like cold storage facilities, data centers, or sports arenas can offer lucrative opportunities.
Innovation and customization Continued advancements in design, materials, and technologies can open doors for personalized and innovative metal building solutions.
Conclusion
The metal building industry is not simply a niche player in the construction landscape; it’s poised for continued growth, innovation, and adaptation. By embracing the trends and opportunities laid out in this outline, the industry can navigate the challenges and solidify its position as a leader in cost-effective, sustainable, and versatile building solutions.The metal building industry’s significance goes beyond its economic impact. It provides solutions for a diverse range of needs.


